Geographic Information Systems (GIS) technology is transforming the landscape of urban planning. By integrating location-based information into planning processes, GIS enables city planners to analyze urban problems and craft precise solutions. This tool has become indispensable in managing city infrastructures and resources, predicting urban trends, and engaging the community. Its diverse applications range from transportation management to environmental protection, underscoring its importance in sustainable urban development. In this blog, we will share insights into how GIS technology is reshaping how cities are planned and managed, ensuring more efficient, sustainable, and responsive urban environments.
Defining GIS Technology
GIS technology is a system used to collect, manage, and analyze information based on geography. It merges location data with descriptive details to create detailed maps and reports. This feature makes GIS a valuable tool for urban planners who need to visualize complex situations to make smart decisions. Additionally, the ability to update GIS data instantly allows planners to react swiftly to changes and emergencies, improving a city’s ability to adapt and stay strong.
Historical Development of GIS in Urban Planning
GIS in urban planning dates back several decades when planners first recognized its potential to improve city layouts and infrastructure systems. Initially, it was used to map cities and understand geographical constraints. As technology advanced, GIS applications became more sophisticated, incorporating real-time data to track urban growth and infrastructure changes. This historical progression has demonstrated the increasing value of GIS in crafting effective urban policies and interventions.
GIS and Educational Advancement
The advancement of GIS technology is significantly bolstered by higher education. Programs like an online masters in GIS provide urban planners with the expertise to apply advanced spatial analysis techniques in real-world scenarios. Such academic programs not only deepen technical skills but also foster innovative thinking about urban challenges. Graduates from these programs are equipped to lead transformative projects in their cities, leveraging GIS to address complex urban issues.
Urban Planning and Development Analysis
GIS is a cornerstone in the development analysis of urban areas, offering tools to simulate urban growth and its impacts. Planners use GIS to conduct feasibility studies and determine the best land use in urban settings, which helps in zoning decisions and land use planning. By analyzing patterns of development, GIS aids urban planners in forecasting future growth, ensuring that the expansion is sustainable and well-integrated with existing infrastructure.
Transportation and Traffic Management
Effective transportation systems are vital for any city, and GIS provides the tools necessary to enhance these systems. Through spatial analysis, GIS helps in designing road networks that minimize traffic congestion and improve safety.
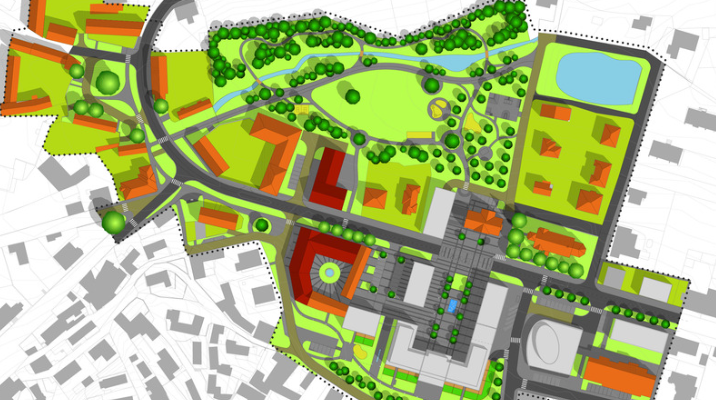
Planners can also use GIS to plan public transportation routes and schedules, optimizing connectivity and accessibility. Additionally, GIS data is crucial for emergency response planning, ensuring that vital services are accessible during emergencies.
Environmental Impact Assessments
In the realm of environmental planning, GIS technology plays a crucial role. It allows urban planners to conduct detailed environmental impact assessments before proceeding with development projects. By mapping environmental data, GIS helps identify areas that are sensitive or at risk, guiding planners in making decisions that mitigate adverse effects on the environment. This proactive approach helps in preserving natural habitats and maintaining biodiversity within urban settings.
Disaster Management and Response
GIS technology is invaluable in managing disasters and improving response strategies. Urban planners utilize GIS to map areas vulnerable to natural disasters like floods, earthquakes, and hurricanes. This mapping allows cities to prepare more effectively by positioning resources where they are likely to be needed most. Additionally, GIS facilitates the coordination of emergency services, ensuring quick and efficient responses when disasters strike. The technology also aids in recovery efforts, helping to assess damage and plan rebuilding initiatives that mitigate future risks.
Public Utilities and Service Delivery
Managing public utilities with GIS leads to more efficient operations and better service delivery. The technology enables city managers to monitor and control the distribution of water, power, and waste services across urban areas. GIS helps identify potential problems before they become critical, such as detecting leaks or predicting areas of high demand. It also supports the development of more efficient routes for garbage collection and maintenance activities, reducing operational costs and improving service timeliness.
Community Engagement and Public Participation
GIS tools have transformed how community input is gathered and utilized in urban planning. By creating interactive maps and visualizations, planners can present complex data in understandable formats, facilitating clearer communication with the public. Residents can use these tools to provide feedback on planning proposals, ensuring their voices are heard and considered in decision-making processes. This open and inclusive approach fosters a stronger sense of community and builds public trust in urban development projects.
Sustainable Urban Development
Sustainability is a key focus in modern urban planning, and GIS is pivotal in promoting environmentally friendly development. Planners use GIS to integrate green spaces into urban designs, optimize building locations to maximize natural light and heat, and monitor environmental compliance. The technology also supports the planning and implementation of renewable energy sources, such as solar panel installations on city buildings. GIS ensures that sustainability is not an afterthought but a foundational aspect of urban planning processes.
Smart Cities and IoT Integration
As cities become smarter, GIS is increasingly integrated with the Internet of Things (IoT) to improve urban life. GIS supports IoT devices that collect data on everything from traffic patterns to air quality, providing a detailed overview of urban health. This integration allows for real-time monitoring and management of city environments, adapting to changes.
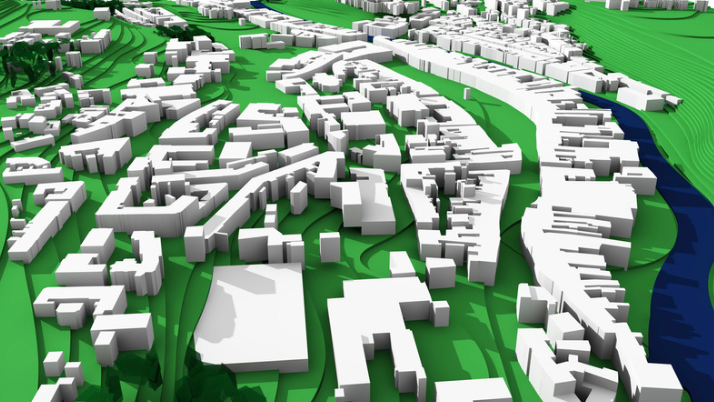
Future trends suggest even greater integration, with predictive analytics enabling cities to anticipate problems before they happen, streamlining city management, and improving residents’ quality of life.
Economic Implications of GIS in Urban Planning
The economic benefits of GIS in urban planning are significant. By improving efficiency in project planning and execution, GIS technology reduces costs associated with urban development. It enables more precise budgeting and resource allocation, minimizing waste and maximizing the impact of investments. Cities that adopt GIS technology often see a return on investment through enhanced public services, better infrastructure management, and more effective use of public funds. This economic advantage makes GIS an indispensable tool in the urban planner’s toolkit.
Conclusion
The role of GIS in urban planning is both transformative and expanding. As technology advances, its potential to improve urban environments becomes even more profound. Urban planners armed with GIS capabilities are better equipped to create adaptive, efficient, and sustainable urban spaces that respond to the needs of their communities. As we look to the future, the integration of GIS in urban planning will continue to play a vital role in shaping our cities, ensuring they are prepared to meet the challenges of tomorrow. This technology is not just about maps and data; it’s about creating a vibrant, livable future for all city dwellers.


