Hyperconverged storage is a component of hyperconverged infrastructure that introduces cloud architecture to IT data centers and supports contemporary corporate applications without requiring separate storage arrays or storage teams. It uses distributed storage methods to keep data safe, accessible, and secure at all times. Compared to conventional infrastructure, hyper-converged storage simplifies storage resource management. It lowers the total cost of ownership, allowing IT administrators to get better storage pricing than public cloud service providers.
What Is Hyper Converged Storage?
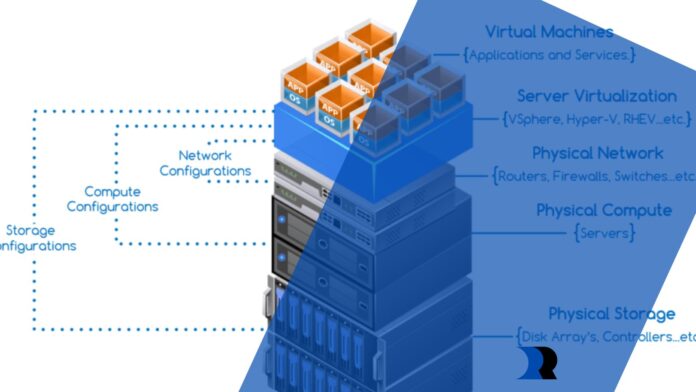
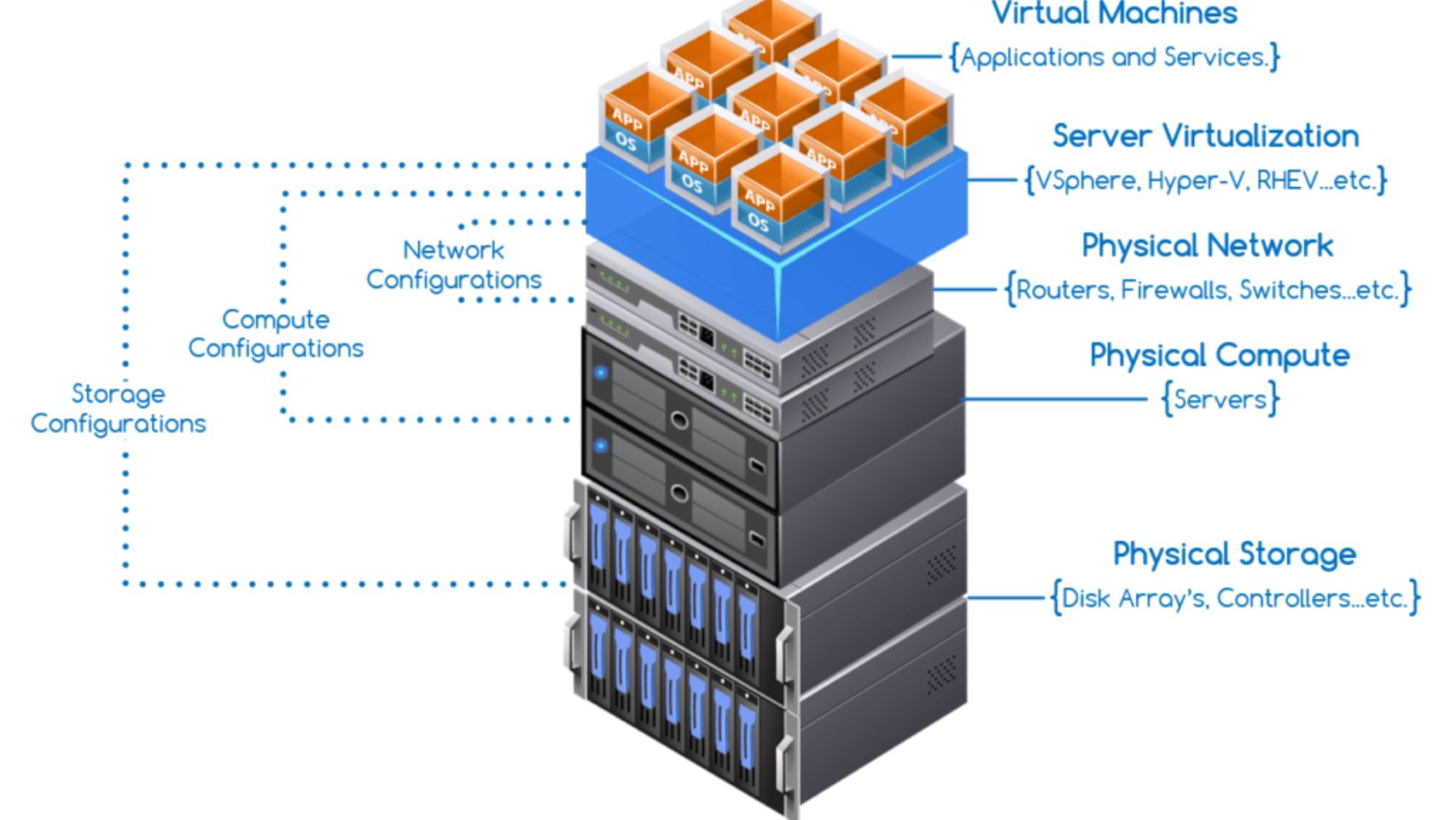
Hyperconverged storage is a subset of hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI), which combines storage, computation, and networking into a single virtualized system. Flexible storage pools replace specific hardware in this software-defined approach. Each node has a software layer that virtualizes the node’s resources and distributes them across all nodes in a cluster, resulting in a single huge storage pool. Load balancing and software-defined networking (SDN) select which hardware will fulfill requests.
Hyperconverged storage simplifies resource management and lowers the total cost of ownership for storage, allowing administrators to get better storage pricing than public cloud service providers in many instances.
Hyperconverged Storage Components
A hypervisor to operate virtual machines, software-defined applications, and virtual networking tools are among the components of hyperconverged storage. Everything can operate on commodity hardware, such as x86 servers, rather than more costly proprietary arrays.
Hyperconverged storage eliminates the need for separate boxes for storage, networking, and computing resources and the requirement to pack each component into a unique piece of hardware suited for a given application. Instead, a software layer on top of everything virtualizes all storage and other resources so that many people and devices may share them.
This results in a storage pool that may include many NAS devices, SAN arrays, and cloud assets managed as a unified entity of closely connected components. Load balancing and software-defined networking technologies, which enable storage arrangement in the ideal location to improve performance and comply with organizational demands, are critical components of hyperconverged storage.
Features of Hyperconverged Storage
With hyper converged storage, there is no need to handle each hardware component individually. Storage is no longer bound to a disk array, a NAS filer, or the cloud, each with its management systems and occasionally operating systems.
Storage is handled and administered at the hypervisor level in a hyper-converged architecture. The hypervisor maintains several storage pools and considers them virtual resources inside a single pool, abstracting the actual hardware. SDS decouples storage resources from the hardware for increased flexibility, efficiency, and scalability.
All storage resources can be integrated into a larger software-defined data center (SDDC) design, which provides automation to overall data center operations and offers more automation and flexibility to storage assets. As a result, application programming interfaces (APIs) can be easily tied into storage to integrate across a broader range of platforms and applications.
Benefits of Hyperconverged Storage
Hyperconverged storage has many significant benefits over standard storage systems.
Automated Provisioning
When providing storage, storage managers used to have to put in a lot of physical effort. Hyperconverged systems make provisioning easier by allowing the administrator to choose performance, capacity, and other factors, and the storage resources are automatically assigned.
Cost
When hardware is removed from the equation, storage costs fall dramatically. Of course, some companies provide hyper-converged solutions on their chosen hardware, but such products are usually competitively priced. Expensive storage hardware is usually only required when a particular machine is designed to execute a certain application.
Flexibility
Storage provisioning is much simpler with hyper-converged storage since no specific physical location or device on which the storage will be hosted is required. This allows storage managers to respond to changing demands more readily.
Ramping
Granular scaling of hyperconverged storage is possible. More storage may be added as needed and withdrawn as quickly as it is no longer required. Companies only pay for what they need.
Downtime
The introduction of software-defined storage and hyper-converged infrastructure has resulted in features such as self-healing, increased redundancy, and increased robustness. This leads to reduced downtime.
Challenges of Hyperconverged Storage
There are a few downsides to hyper-converged storage to consider.
Vendor Lock-In
Adopting hyper-converged storage often means being enslaved to a single vendor ecosystem.
Not all suppliers force customers to utilize pre-defined hardware; if choice is vital, it may be worth looking for a provider that provides various suitable alternatives.
Performance
Hyperconvergence generally provides excellent performance; however, specific workloads, such as high-performance computing (HPC) and generative artificial intelligence (AI), may not benefit from hyper converged storage. There are hyperconverged systems that achieve exceptional performance by tailoring software, storage, networking, computing, and memory to execute a particular workload or application.
Migration
It may be tough to move your data after it has been placed in a hyper-converged storage system. While that solution has some flexibility, it has less when migrating data to or from it.
Capacity
It may be tough to move your data after it has been placed in a hyper-converged storage system. While that solution has some flexibility, it has less when migrating data to or from it.
Additional Layers
While hyper-converged storage simplifies life in many ways, it adds another degree of complexity. Those trained in conventional storage may need further instruction to master it.
Use Cases of Hyperconverged Storage
A variety of applications benefit from hyper converged storage. Here are some of the most typical:
● Virtual machines. Because virtualization lends itself well to SDS-based infrastructure, hyper-converged storage is an ideal home for many virtual machines (VMs).
● Databases. Several databases perform well in hyper-converged storage; several manufacturers provide boxes dedicated to their databases, including a full hyperconverged infrastructure solution that includes storage, computing, networking, and apps.
● Virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI). Desktop virtualization is a method of separating the desktop environment, as well as the accompanying apps and data, from the actual client device that has historically been used for access. Because no data is stored locally in the user workstation, the different desktop components are virtualized, providing better flexibility and easier disaster recovery.
● Data protection. Hyperconverged storage is an excellent way to unify all storage resources in one virtual pool to simplify data protection. The software can back everything up in the pool from one interface; similarly, disaster recovery (DR) can be implemented across hyper converged storage instead of manually configuring each physical storage device for backup and DR.
● Branches. Some businesses have branch offices backed by centralized, offsite IT—hyper-converged storage may be a suitable match for branch office installations since the infrastructure can be remotely monitored.
Conclusion
Hyperconverged storage is gaining popularity and performs well in a variety of applications. In the big scheme of things, IT infrastructure is becoming more virtualized. Storage has progressed from a labor-intensive IT function to a more generic IT duty. Hyperconverged storage makes scalable storage more accessible to a broader range of enterprises without requiring them to depend on skilled storage teams.